Introduction to Animal and Plant Whole Genome Sequencing
Animal and Plant Whole Genome Sequencing(WGS) is an instrumental technique that is commonly employed to sequence the entire genomes of animals and plants, respectively, and aims at identifying genomic variations such as SNP, InDel, CNV, and SV. Whole Genome Sequencing is an ideal approach to determine the entirety of genetic information at a single nucleotide level.
Novogene offers Animal and Plant Whole Genome Sequencing services with ultra-fast turnaround time, high-quality sequencing data, and reliable results. Animal and Plant Whole genome sequencing has found its applications in several fields including population genetics research, genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and agricultural breeding programs.
Unleashing Genetic Insights with Novogene: Plant and Animal Whole Genome Sequencing Solutions
- Genetic Research and Discovery: WGS uncovers genetic variations and novel genes, advancing our understanding of traits, diseases, healthcare and veterinary medicine.
- Evolutionary Biology: WGS unveils genomic changes over time, shedding light on evolutionary processes and mechanisms driving genetic adaptations and speciation.
- Crop Improvement and Breeding: WGS identifies genetic markers for desirable traits, revolutionizing crop breeding programs and enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Phylogenetics and Taxonomy: WGS elucidates evolutionary relationships and species classification, enriching our understanding of biodiversity and evolutionary history.
- Conservation Biology: WGS assesses genetic diversity and population structure, informing conservation strategies to preserve endangered species and maintain ecosystem health.
Why Choose Novogene for Your Plant&Animal WGS Needs?
- Industry-Leading Expertise: With years of experience and a team of skilled professionals, Novogene has extensive experience with a wide range of plants and animals such as pigs, mice, tigers and bees.
- Quality Assurance: Novogene maintains strict quality control measures throughout the entire sequencing process to deliver Illumina data with Q30≥85% and PacBio Revio bases with Q30≥90%.
- Cost-effective Service: Our streamlined processes and efficient workflows ensure rapid and efficient genome-wide profiling of multiple samples at a very competitive price.
- Comprehensive Services: Novogene offers customized and advanced solutions tailored to meet your specific research or genome-wide association study.
Animal and Plant WGS Specifications:
DNA Sample Requirements
| Platform Type | Sample Type | Amount (Qubit®) | Purity |
| Illumina
NovaSeq X Plus /NovaSeq6000 |
Genomic DNA | ≥ 200 ng | OD260/280=1.8-2.0;
no degradation, |
| Genomic DNA
(PCR free customized) |
≥ 3 μg | ||
| Genomic DNA
(PCR free) |
≥ 1.1 μg | ||
| PacBio Revio DNA HiFi library | HMW Genomic DNA | ≥ 3 μg | A260/280=1.75-2.0; A260/230=1.5-2.6; *NC/QC=1.0-2.2 Fragments should be ≥ 30 kb |
| PacBio PCR product library |
PCR product | ≥ 2 μg | OD260/280=1.75~2.0; OD260/230=1.4~2.6; *NC/QC=0.95~3.00; Single band (PacBio library fragments distributed above 1k) |
| Nanopore PromethION DNA library |
HMW Genomic DNA | ≥ 8 μg | A260/280=1.75-2.0; A260/230=1.4-2.6; *NC/QC=0.95~3.00 Fragments should be ≥ 30 kb |
| Nanopore Ultra-long DNA Library | uHMW Genomic DNA (plant and animal tissues) | ≥ 20 μg | OD260/280=1.7-2.0; OD260/230=1.3-2.6; *NC/QC=0.95-3.00; Fragments should be ≥ 100k, no fragments below 30k. |
| Nanopore PCR product library |
PCR product | ≥ 2 μg | OD260/280=1.75~2.0; OD260/230=1.4~2.6; *NC/QC=0.95~3.00; Single band |
*NC/QC = NanoDrop concentration/Qubit concentration
Animal and Plant WGS Specifications: Sequencing and Analysis
| Platform Type | Illumina NovaSeq X Plus /NovaSeq6000 | PacBio Revio/sequel II/sequel IIe | Nanopore PromethION |
| Read Length | Paired-end 150 bp | Average > 15 kb | Average > 17 kb |
| Recommended
Sequencing Depth |
For SNP/InDel detection: ≥ 10× | For SV detection: ≥ 20× | |
| For SV/CNV detection: ≥ 20× | |||
| Content of
Analysis |
Standard Analysis
Advanced Analysis
|
Standard Analysis
|
|
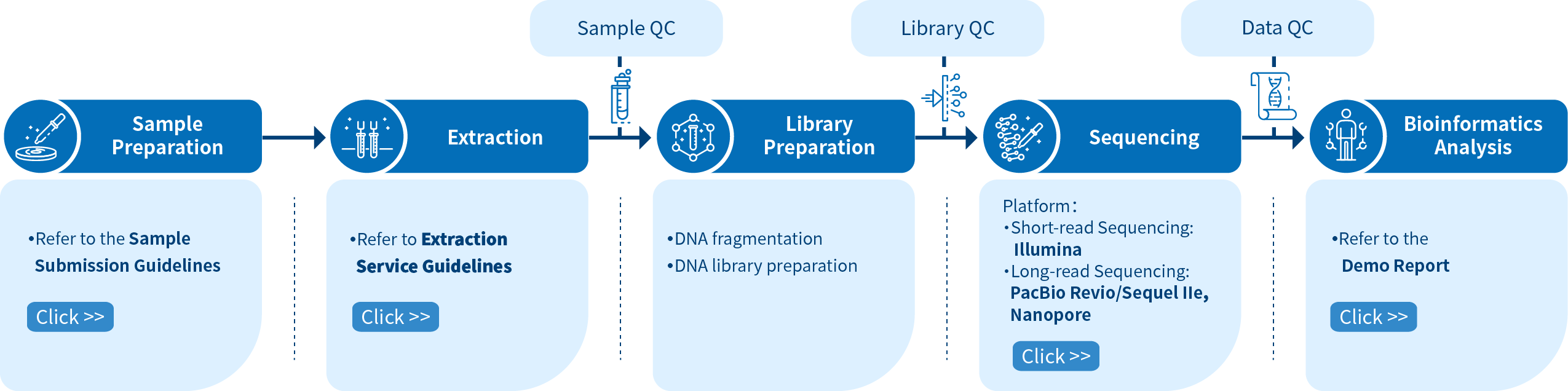
Novogene Workflow of Animal and Plant Genome Sequencing Service
From sample and library preparation, short and long-read sequencing, and data quality control, to bioinformatics analysis, Novogene provides high-quality products and professional services. Each step is performed in agreement with a high scientific standard and meticulous design to ensure high-quality research results.
Featured Publications using Novogene’s Animal and Plant WGS service
Case Studies
-
Seagrass genomes reveal ancient polyploidy and adaptations to the marine environment
Journal: Nature PlantsIssue Date: 26 January, 2024IF: 18.0DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-023-01608-5
-
A population of stem cells with strong regenerative potential discovered in deer antlers
Journal: ScienceIssue Date: 23 February, 2023IF: 56.9DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.add0488
-
Genomic selection and genetic architecture of agronomic traits during modern rapeseed breeding
Journal: Nature GeneticsIssue Date: 28 April, 2022IF: 30.8DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01055-6
-
The genomic basis of geographic differentiation and fiber improvement in cultivated cotton
Journal: Nature GeneticsIssue Date: 15 April, 2021IF: 30.8DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00844-9
-
Resequencing of 1,143 indica rice accessions reveals important genetic variations and different heterosis patterns
Journal: Nature CommunicationsDate: 22 September, 2020IF: 12.121DOI:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-18608-0
-
Journal:Plant Biotechnology JournalIssue date: 18 September, 2020IF: 8.154DOI: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/pbi.13480
Demo Result
Sequencing Quality Distribution
Sequencing quality distribution is examined over the entire length of all sequences, to detect regions where incorrect bases are incorporated at abnormally high levels. The detailed sequencing quality distribution is as follows.
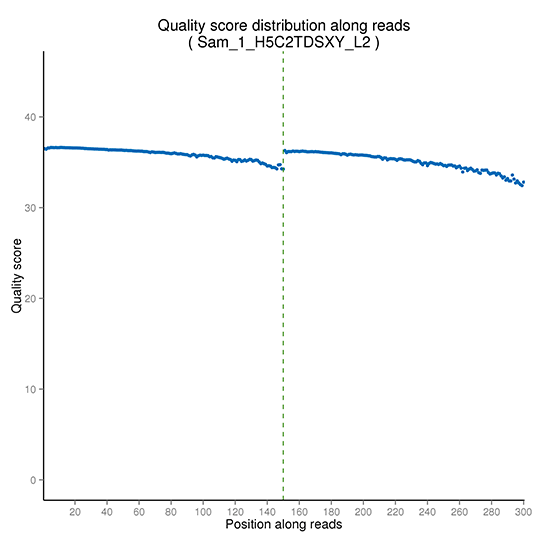
Distribution of sequencing quality
Note: The x-axis shows the base position within a sequencing read, and the y-axis shows the average phred score of all reads at each position.
(Pair-end sequencing data are plotted together, with the first PE150 bp representing read 1 and the following PE150 bp for read 2.)
Sequencing Error Rate
The sequencing error rate is the major confounding factor of precise detection of low-frequency variations by deep sequencing. It determines the quality of the sequencing data. The sequencing error rate is highly associated with the sequencing cycle, escalating towards the end of each read because of the consumption of chemical reagents, which is a common feature of the Illumina high throughput sequencing platform.
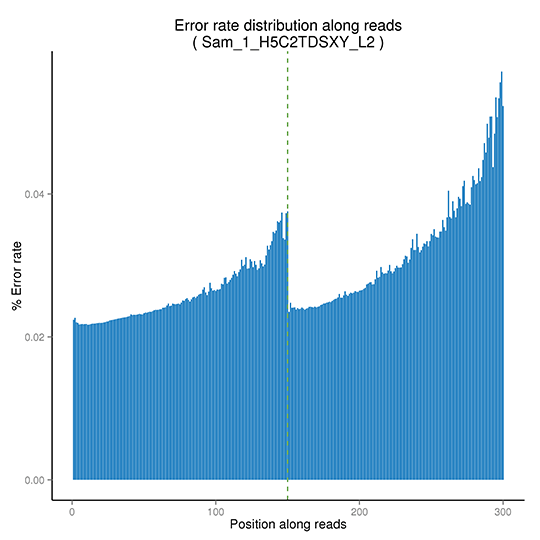
Distribution of sequencing error rate
Note: The x-axis shows the base position along each sequencing read and the y-axis shows the base error rate.
(Pair-end sequencing data are plotted together, with the first PE150 bp representing read 1 and the following PE150 bp describes read 2.)
Filtering reads containing adapter or with low quality
The sequencingraw reads often contain low-quality reads or reads with adaptors, which influences the quality of the downstream analysis. To avoid this, it is necessary to filter out the raw reads and obtain clean reads. Raw reads filtering should be done under the following conditions:
(1) Remove the paired reads when either read contains adapter contamination;
(2) Remove the paired reads when uncertain nucleotides (N) constitute more than 10 percent of either read;
(3) Remove the paired reads when low quality nucleotides (base quality less than 5, Q ≤ 5) constitute more than 50 percent of either read.
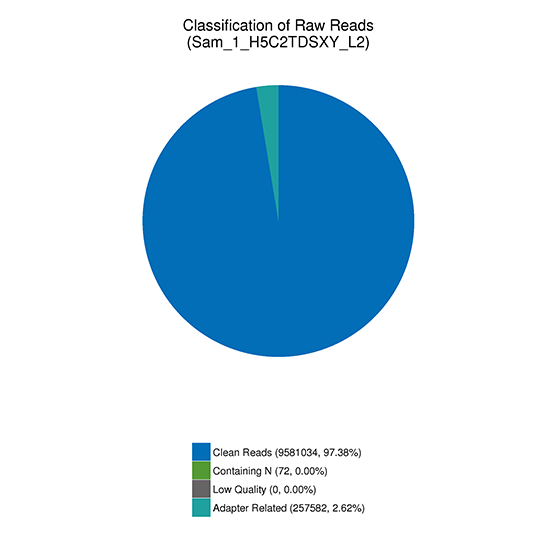
Note:
Classification of the sequenced reads
(1) Adapter related: (reads containing adapter) / (total raw reads).
(2) Containing N: (reads with more than 10% N) / (total raw reads).
(3) Low quality: (reads of low quality) / (total raw reads).
(4) Clean reads: (clean reads) / (total raw reads).
Alignment with reference genome
Mapping Statistics with Reference Genome
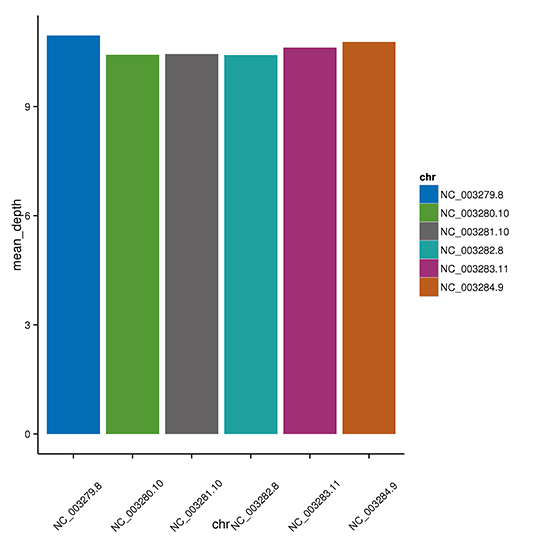
The mean depth of each chromosome.
Note: The x-axis shows the chromosome and the y-axis shows the mean depth
Standard Analysis
SNP Detection & Annotation
ANNOVAR is a software that efficiently annotates genetic variants spotted from the genome utilizing contemporary information. Provided an index of variants with reference nucleotide, start position, end position, observed nucleotides, and chromosome, ANNOVAR can perform gene-based annotation, region-based annotation, filter-based annotation as well as other functionalities.
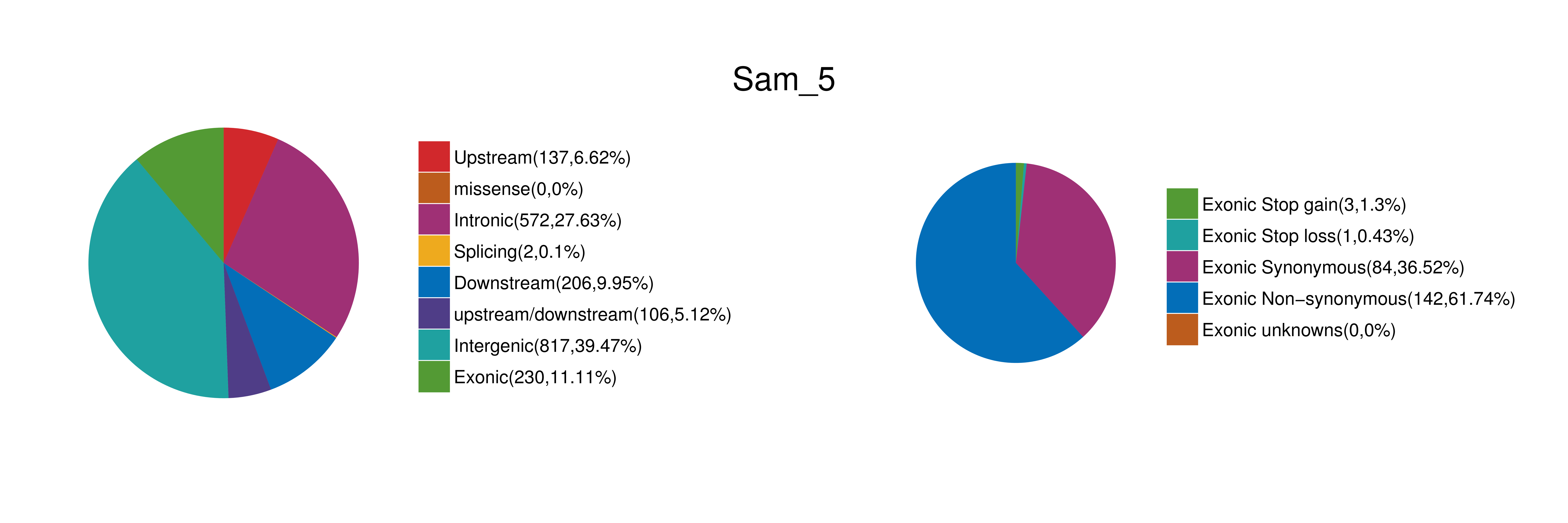
Note: The figure demonstrates the distribution of (A) The number of SNPs in different regions of the genome (left) and (B) the number of SNPs of different types in the coding region (right)
SNP Quality Distribution
To assess the credibility of detected SNPs, we checked the distribution of support reads number, SNP quality, as well as the distance between adjacent SNPs. The results as follows.
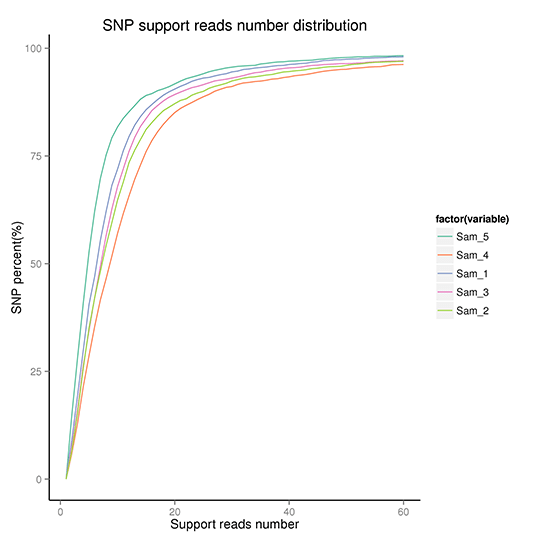
Cumulative distribution of SNP quality
Note: These figures demonstrate the quality distribution of SNPs, distribution of SNP support reads number, distribution of distances between adjacent SNPs, and the cumulative distribution of SNP quality.
SNP Mutation Frequency
Take the T:A>C:G mutations as an example, this category includes mutations from T to C and A to G. When T>C mutation appears on either of the double-strand, the A>G mutation will be found in the same position of the other chain. Therefore the T>C and A>G mutations are classified into one category. Accordingly, the whole-genome SNP mutations could be classified into six categories.
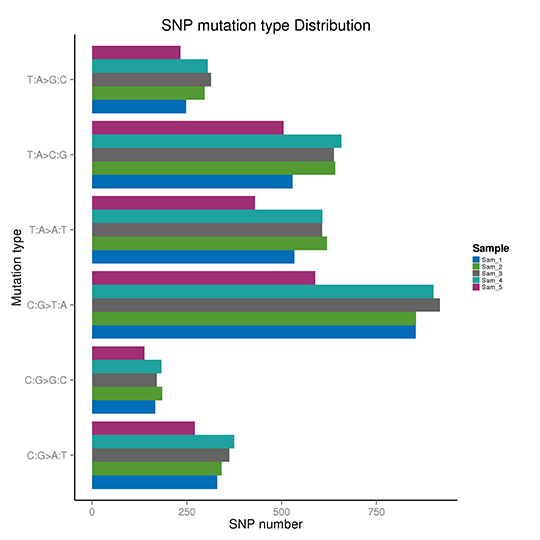
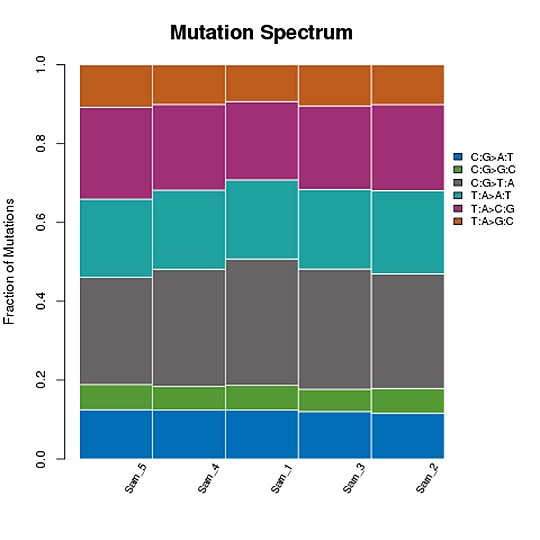
Frequency of SNP mutations
Note:The x-axis represents the number of the SNPs, and y-axis indicates the mutation types.
CNV Detection & Annotation
Copy-number variation (CNV) is a type of structural variation that happens when a DNA fragment is present in variable copy number in comparison to a reference genome. It pinpoints the deletions and duplications in the genome. Based on the reads depth of the reference genome, CNVnator can be used to detect CNVs of potential deletions and duplications with the following parameter ‘-call 100’. The detected CNVs are then further annotated by ANNOVAR.
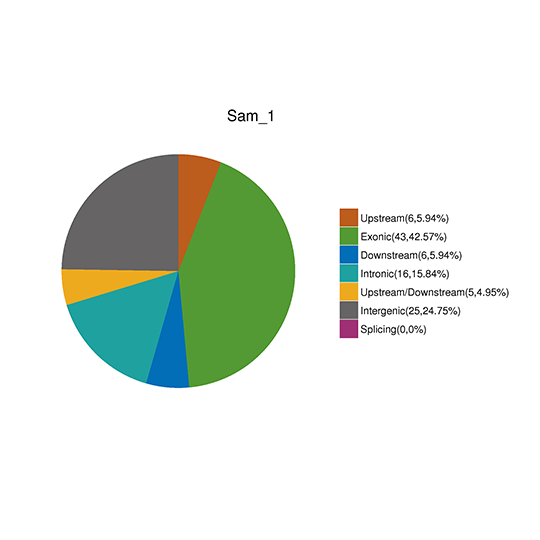
CNV annotation
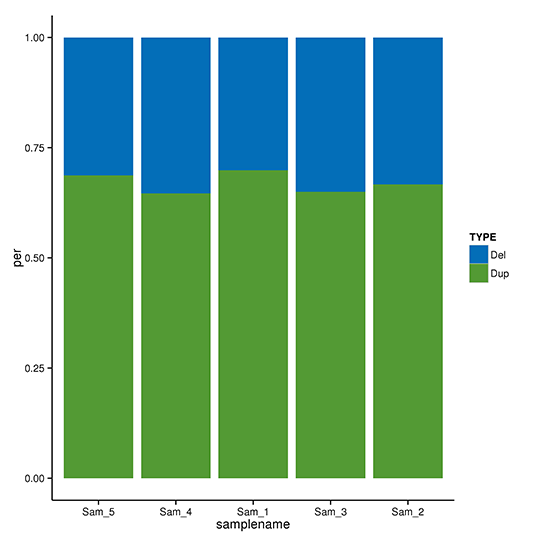
Ann Variation type statistics distribution of CNVs
Note:The x-axis represents samples, and the y-axis indicates the proportion of each type of CNVs.
*Please contact us to get the full demo report.