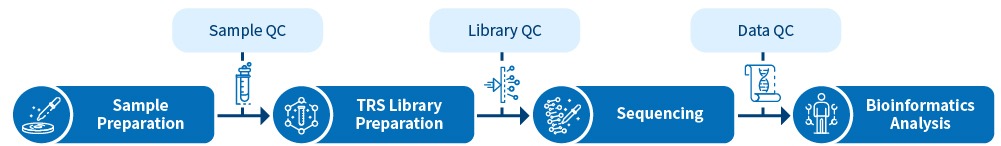
What is Target Region Sequencing?
Target Region Sequencing (TRS) focuses on a subset of genes or specific regions of the genome, which are most likely to be associated with a disease or phenotype-related studies. It is used for analyzing mutations in a given sample. Compared to Whole Genome Sequencing and Whole Exome Sequencing, target region sequencing generates more comprehensive and manageable data and is more cost-effective in investigating regions of interest, achieving delivery of much higher coverage and identification of rare variants.
Novogene’s target region sequencing provides comprehensive services including customized panel design, library preparation, sequencing, and bioinformatics analyses based on your research purpose.
Applications of Target Region Sequencing
- Cancer research
- Human population studies
- Linkage analysis for inherited diseases
- Detection and quantification of low-frequency alleles and rare variants
- Detection of somatic and germline mutations
- Discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets
Benefits of Target Region Sequencing
- Agilent SureSelectXT Custom Kit and NovaSeq 6000 platforms are available for TRS service.
- Data quality with a guarantee of Q30≥85%.
- Compact and manageable data set for bioinformatics analyses.
- Much more economical with a capacity of processing large number of samples.
- Ready-for-publication data and figures bring the simple insights for the result overview based on Novogene cutting-edge bioinformatics pipeline and database.
TRS Specifications: Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Amount (Qubit®) | Purity |
| Genomic DNA | ≥ 300 ng | A260/280=1.8-2.0 no degradation, no contamination |
| Genomic DNA from FFPE | ≥ 400 ng | Fragments should be longer than 1000 bp |
| cfDNA / ctDNA | ≥ 35 ng | Fragments should be in multiples of 170bp, with no genomic contamination |
TRS Specifications: Sequencing and Analysis
| Platform Type | Illumina NovaSeq 6000 | ||||
| Read Length | Paired-end 150 bp | ||||
| Sequencing depth | Average effective sequencing depth above 200× | ||||
| Standard data analysis |
|
||||
Note: For detailed information, please refer to the Service Specifications and contact us for customized requests.
Featured Publications of TRS Sequencing
-
The Spectrum of mitochondrial genomic variation in parathyroid neoplasms
Endocrine Date: July 2021IF: 21.674DOI: 10.1007/s12020-021-02825-8
-
Journal of HepatologyIDecember Date: 2019IF: 20.582DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.07.014
-
Genetic Alterations in Esophageal Tissues From Squamous Dysplasia to Carcinoma
Gastroenterology Date: July 2017IF: 18.392DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.033
Data Quality Control
Sequencing Error Rate Distribution
The sequencing error rate is the major confounding factor of precise detection of low-frequency variations by deep sequencing. It determines the quality of the sequencing data. The sequencing error rate is highly associated with the sequencing cycle, escalating towards the end of each read because of the consumption of chemical reagents, which is a common feature of the Illumina high throughput sequencing platform.
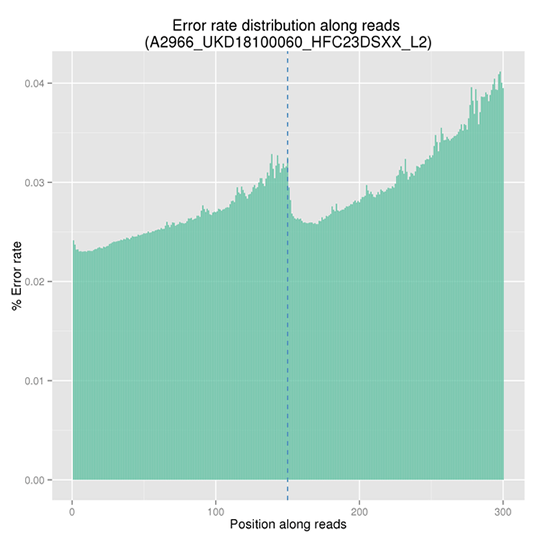
Note:
The x-axis represents the position in reads, and the y-axis indicates the average error rate of bases of all reads at a position.
GC Content Distribution
GC content distribution aims to check the potential of AT/GC separation. Sample contamination, sequencing bias, and errors during library preparation can impact on the sequencing results.
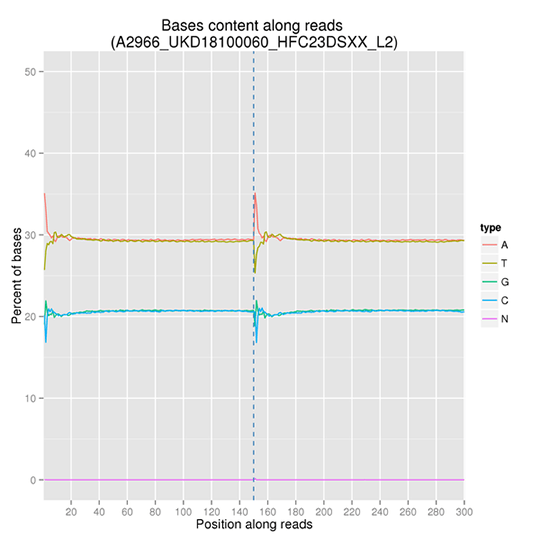
Note:
The x-axis represents the position in reads, and the y-axis indicates the percentage of each type of bases (A, T, G, C); different bases can be distinguished by different colors.
SNP and InDel calling, annotation and statistics
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), also known as single nucleotide variants (SNVs), constitute the largest class of genetic variants in the genome. Another class of genetic variations includes small insertions and deletions (InDels) which are <50 bp in length.
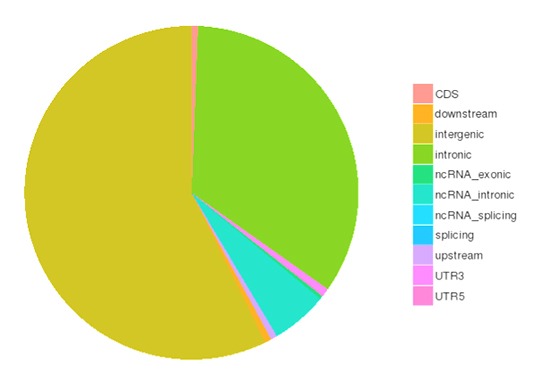
The number of SNPs/InDels in various genomic regions
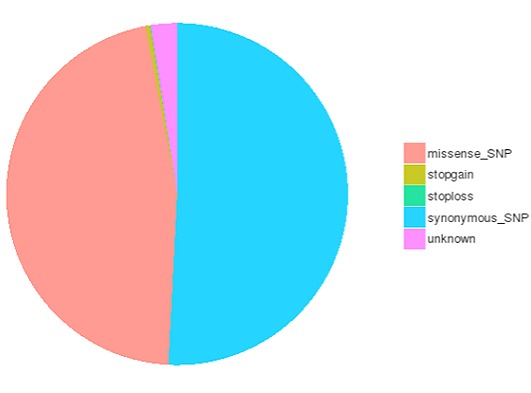
The number of different types of SNPs/InDels in coding region
*Please contact us to get the full demo report.