Utilising QIIME 2 pipeline: a current and future golden standard platform to analyze Amplicon-Seq data
Amplicon Analysis
QIIME 2 is nowadays used as a next-generation microbiome bioinformatics platform that is extensible, free, open source, and community developed. As a powerful, scalable and decentralized microbiome analysis resource, it emphasizes transparency in data analysis of Amplicon-Seq data (e.g 16S rRNA gene), and pays more attention to interactive and visual image display. As it provides its users with an end-to-end pipeline to analyze Amplicon Sequencing data, QIIME 2 represents the golden standard for future microbiome analysis methods.
The microbiome field has undergone a shift from clustering-based methods of operational taxonomic unit (OTU) designation based on sequence similarity (Uparse) to denoising algorithms (DADA2 and Deblur) that identify exact amplicon sequence variants (ASVs).
At present, DADA2, Unoise3 and Deblur are three widely used noise reduction analysis tools. Unoise3 was developed by Robert Edgar to make up for 97% out clustering defects. Another novel method to obtain OTU without clustering is deblur published in 2016. This method has been used to process the global data obtained by the earth microbiome program, which was published in Nature in November 2017. DADA2 can only operate on mixed samples. Deblur’s advantage is that it can operate not only on mixed samples, but also on a single sample. Deblur resolution can also achieve single nucleotide accuracy.
Novogene QIIME 2
Novogene has developed the whole-process QIIME2 analysis, including ASVs analysis and species annotation, α-diversity, β-diversity, species difference and symbol species analysis, as well as functional prediction.
1.Accurate Annotation
Errors in Illumina-sequenced amplicon data are currently addressed by quality filtering and the construction of operational taxonomic units (OTUs). DADA2 infers sample sequences exactly and resolves differences of as little as 1 nucleotide. Each de-duplicated sequence generated after noise reduction using DADA2 is called ASVs (Amplicon Sequence Variants).
Comparison of QIIME 2 vs QIIME 1
| ASV (QIIME 2) | OTU (QIIME 1) | |||
| Compare sequence similarity (~99%) | Clustering at 97% similarity | |||
|
Taxonomy annotation on exact sequence
|
||||
| Taxonomy annotation on representative sequence | ||||
| Higher microbial diversity resolution (Up to species level) | Lower microbial diversity resolution | |||
| Read quality has higher impact on downstream analysis | Read quality has lower impact on downstream analysis | |||
| Readily compared between studies | Reanalysis is required if new data is added | |||
2.Traceable and Repeatable Results with Reproducibility
Automatically track your analyses with decentralized data provenance — no more guesswork on what commands were run! QIIME2 iteratively records data provenance, ensuring bioinformatics reproducibility. You can also easily share results with your team, even those members without QIIME 2 installed.
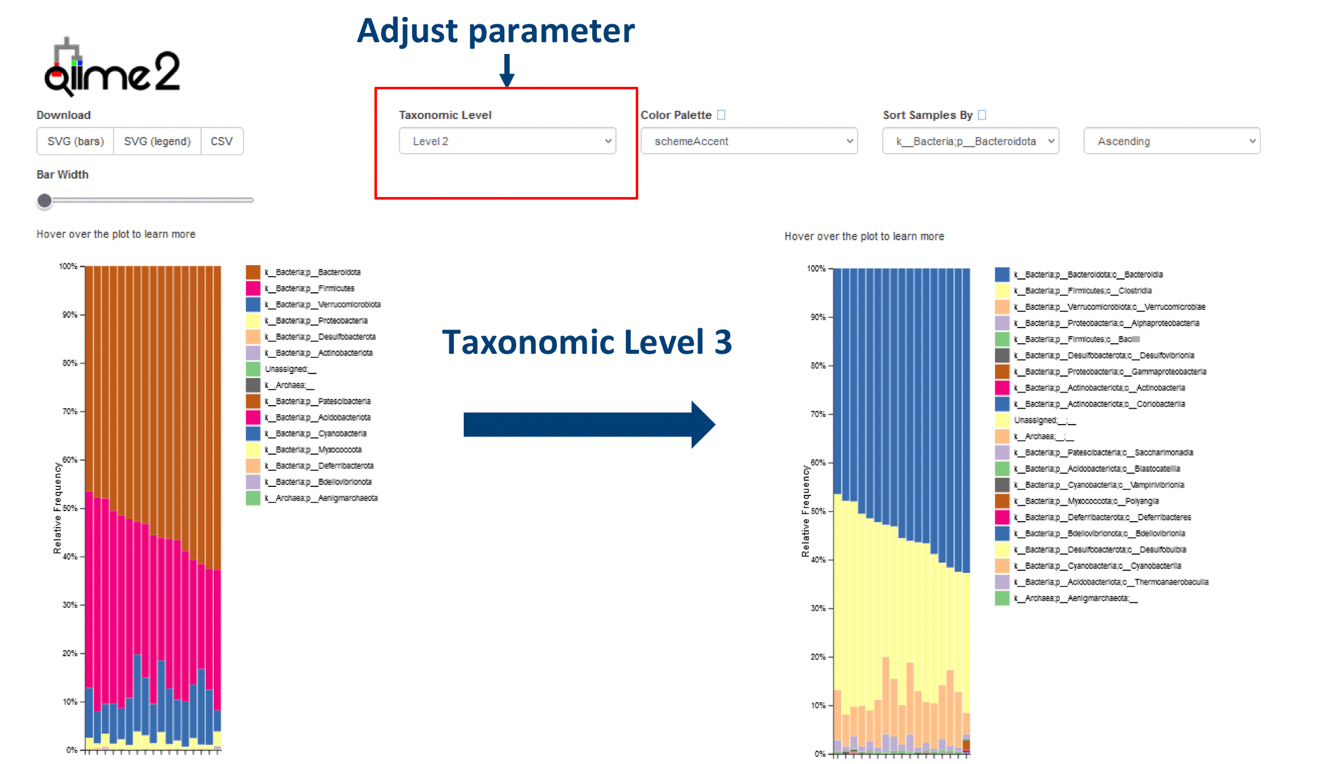
3. Interactive Visualization
Modify your data diagrams with variable parameters that provide new perspectives.
4. Plugin-based System — multiple microbiome analysis all in one
QIIME2 has more than 20 kinds of plugins, and is still under development, in order to provide more perfect services.
5. Data Combination of Different Batches
QIIME2 analyze bases on the exact sequence, merge analysis without re clustering, directly merge the feature sequence abundance table to carry out the follow-up standard analysis. Therefore, different batches of data can be directly combined for analysis.
Novogene has rich experience with Amplicon sequencing projects and Amplicon sequencing services can help retain a great level of flexibility in the experimental design to get analysis and clustering by both OTU (operational taxonomic units) and ASV (DADA2) pipelines. At Novogene, customized analysis can also be available on the online QIIME 2 platform based on your own needs.
In case you are interested in your next microbiome analysis journey, please refer to the for additional information or contact us here.
Reference:
- Bolyen, E., Rideout, J.R., Dillon, M.R. et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37, 852–857 (2019).https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
- Edgar R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10):996.
- Callahan, B., McMurdie, P., Rosen, M. et al. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13, 581–583 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
- Edgar,R.C.(2016) UNOISE2: improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing.doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/081257
- Moossavi S , Sepehri S , Robertson B , et al. Composition and Variation of the Human Milk Microbiota Are Influenced by Maternal and Early-Life Factors[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2019, 25(2):324-335.e4.