Introduction to Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing
16S Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing, 18S Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing, and 16S/18S/ITS Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing are ultra-deep DNA sequencing method that focuses on sequencing specific target regions (amplicons). Short (<500 bp) hypervariable regions of conserved genes or intergenic regions are amplified by PCR and analyzed by next generation sequencing (NGS) technology, to identify and differentiate multiple microbial species from complicated samples.
Amplicon sequencing is designated to sequence the target genes of 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA), or 18S rRNA and Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) rRNA by universal primers. Through utilizing 16S rRNA gene sequencing, 18S rRNA gene sequencing, and ITS rRNA gene sequencing, research can describe and compare the phylogeny and taxonomy of bacteria (and archaea) and fungi (such as yeasts, molds and etc.), respectively.
Novogene’s amplicon sequencing services provide to efficiently screen for variants and target organisms, and describe and compare the diversity of multiple complex environments. The approach is frequently used in population and community microbial ecology studies, phylogenetic reconstruction of target microbial groups, identification of individual species in pure cultures, and detection of organisms of interest (pathogens or beneficial), among many others.
How does of 16S/18S/ITS Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing work?
Amplicon metagenomic sequencing is an effective way to investigate all microorganisms present in diverse samples, including:
- Targeting and identifying the organisms of interest
- Annotating and classifying plentiful microorganisms in one assay, to obtain a complete composition of microbial communities
- Distinction of bacteria and archaea (16S), or fungi and other eukaryotes (ITS/18S)
- Detection of pathogens, microorganism contamination, soil bacterial benefits and etc.
- Analyzing samples from physiological fluids or tissues to diagnose disease and cancers
Advantages of Novogene Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing
Amplicon metagenomic sequencing is considerably simpler, faster and more efficient, compared with the whole microbial genome sequencing by separating each single species in the samples. Based on its highly targeted characteristics and multiplexing, information on thousands of amplicons is obtained by specific amplification in a single run without host contamination. High coverage is achieved, and resequencing is possible even in GC-rich regions.
Novogene has rich experience with amplicon projects and recently developed new pipelines to sequence amplicons using both short reads and long reads (full-length) technology for 16S and 18S amplicons. At Novogene, Amplicon metagenomic sequencing services can help retain a great level of flexibility in the experimental design to get analysis and clustering by both “OTU” (operational taxonomic units) and ASV (DADA2) pipelines. Customized analysis can also be available on the online Qiime 2 platform at will.
Primers applied to Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing
| Types | Amplified Region | Fragment Length | Primers | Sequences (5’- 3’) |
| Bacterial 16S | V4 | 300 bp | 515F | GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA |
| 806R | GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT | |||
| V3-V4 | 450 bp | 341F | CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG | |
| 806R | GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT | |||
| V4-V5 | 450 bp | 515F | GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA | |
| 907R | CCGTCAATTCCTTTGAGTTT | |||
| V5-V7 (for endophytic) | 400-500 bp | 799F | AACMGGATTAGATACCCKG | |
| 1193R | ACGTCATCCCCACCTTCC | |||
| Archaeal 16S | V4-V5 | 400-500 bp | Arch519F | CAGCCGCCGCGGTAA |
| Arch915R | GTGCTCCCCCGCCAATTCCT |
| Types | Amplified Region | Fragment Length | Primers | Sequences (5’- 3’) |
| Fungal 18S | V4 | 350 bp | 528F | GCGGTAATTCCAGCTCCAA |
| 706R | AATCCRAGAATTTCACCTCT | |||
| Fungal ITS | ITS1 | 200-400 bp | ITS5-1737F | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG |
| ITS2-2043R | GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC | |||
| ITS2 | 380 bp | ITS3-2024F | GCATCGATGAAGAACGCAGC | |
| ITS4-2409R | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | |||
| ITS1-1F (for endophytic) | 200-400 bp | ITS1-1F-F | CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA | |
| ITS1-1F-R | GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC |
Amplicon Specifications: DNA Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Amount | Volume | Concentration | Purity |
| Total DNA | ≥ 200 ng | ≥ 40 μL | ≥ 5 ng/μL | A260/280 = 1.8-2.0 |
Note: Sample amounts displayed are for reference only. Download the Service Specifications to learn more. For detailed information, please contact us.
Amplicon Specifications: Sequencing and Analysis
| Sequencing Platform | Illumina NovaSeq 6000 | |
| Read Length | Paired-end 250 bp | |
| Data Output | 30K/50K/100K raw tags | |
| Qiime1 or Qiime2 | Standard Data Analysis |
|
| Advanced Analysis |
|
|
Note: Analysis contents displayed are for reference only. Download the Service Specifications to learn more. For detailed information, please contact us with your customized requests.
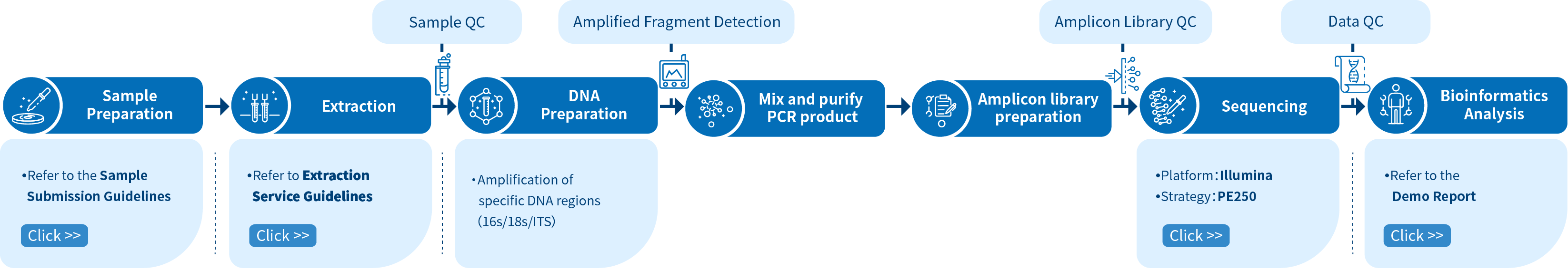
Project Workflow of Novogene Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing Services
The workflow for a new project begins with sample preparation and subsequent quality control. Once the quality of the DNA sample has been validated, PCR amplification will be performed on target regions (amplicons). The amplicons are then purified for library preparation, after which, library quality control commences. Sequencing by synthesis (SBS) technology is used by the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform to sequence the library and, once sequencing is complete and data quality control is performed, bioinformatics analysis is conducted to obtain high-quality results and create publication-ready figures.
Publications with Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing
Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing is a powerful tool for researchers aiming at the identification and differentiation of microbial species, either using OTUs or ASVs. With 16S/18S/ITS rRNA sequencing results, the microbial diversity of the environment through the Alpha (α) and Beta (β) diversity analysis can be characterized, to identify, describe, and track microorganisms of interest. Here is a list of featured publications that have used Novogene Amplicon Metagenomic Sequencing services.
-
Cell Host & MicrobeIssue Date: 10 April 2019IF: 15.923DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.02.003
-
Bioresource TechnologyIssue Date: January 2019IF: 7.539DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.10.045
-
MicrobiomeIssue Date: 03 April 2018IF: 11.607DOI: 10.1186/s40168-018-0441-4
-
Nature CommunicationsIssue Date: 09 January 2017IF: 12.121DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13839
-
Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension
MicrobiomeIssue Date: 01 February 2017IF: 11.607DOI: 10.1186/s40168-016-0222-x
Results of OTU Cluster & Annotation Analysis
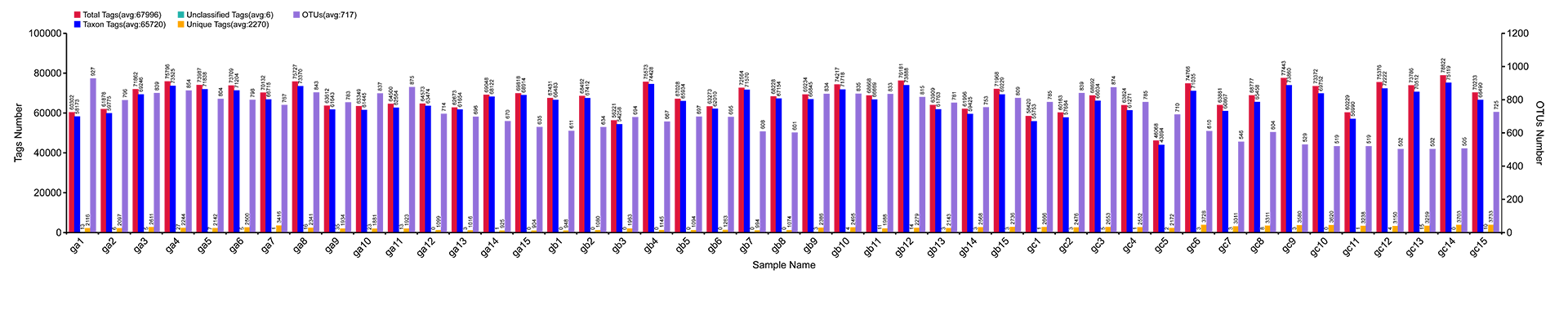
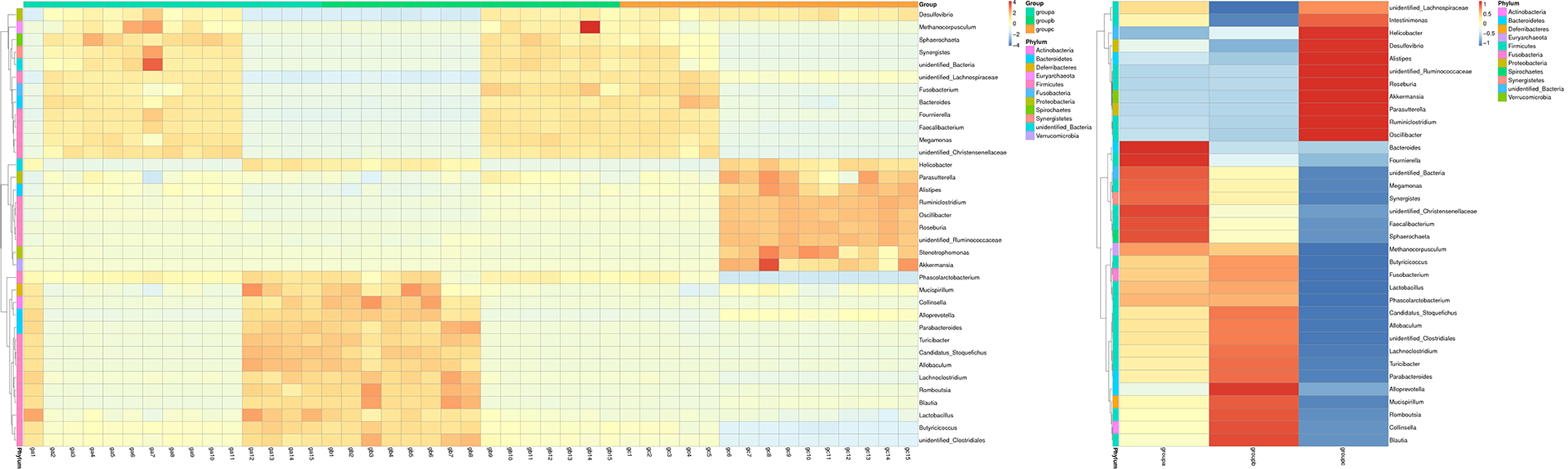
Species Abundance Heatmap
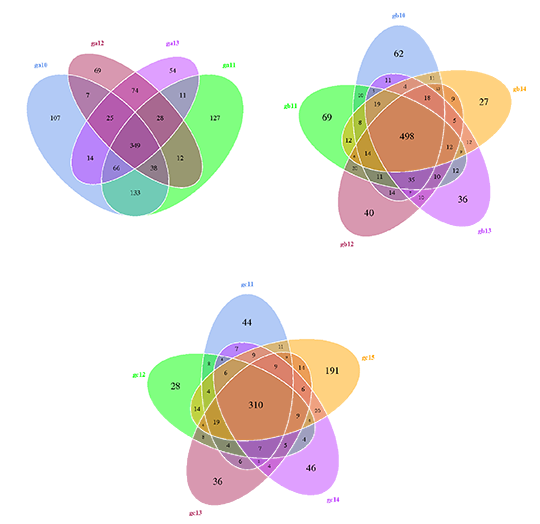
Venn Diagram
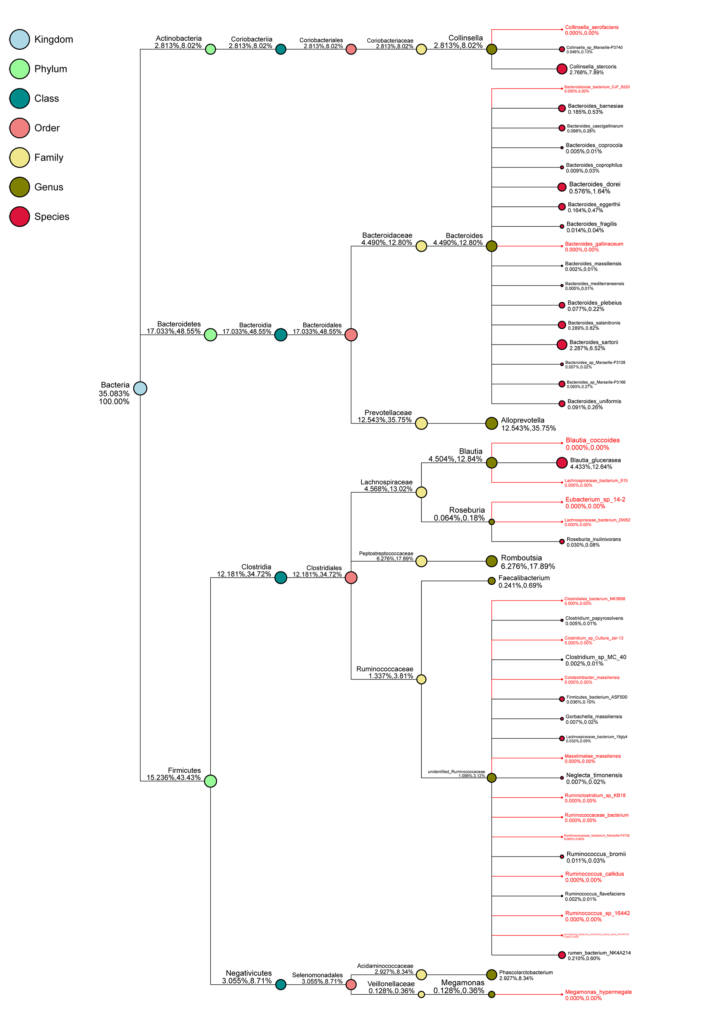
Taxonomy Tree for A Single Sample
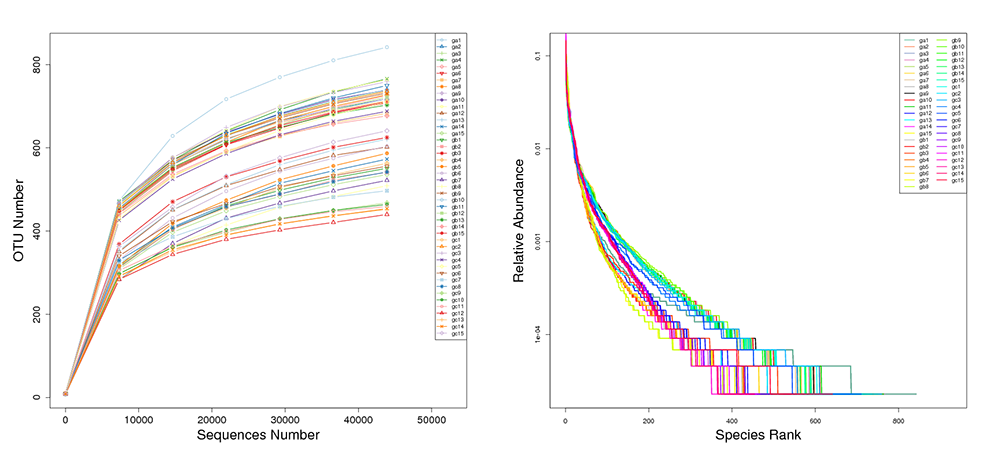
Rarefaction & Rank Abundance Curves by Individual Sample
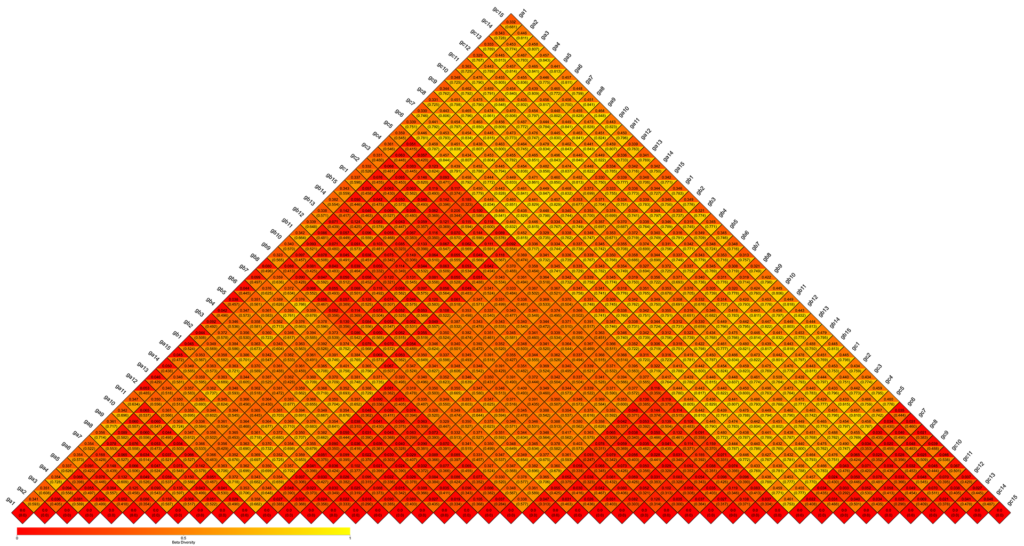
β-diversity Heatmap
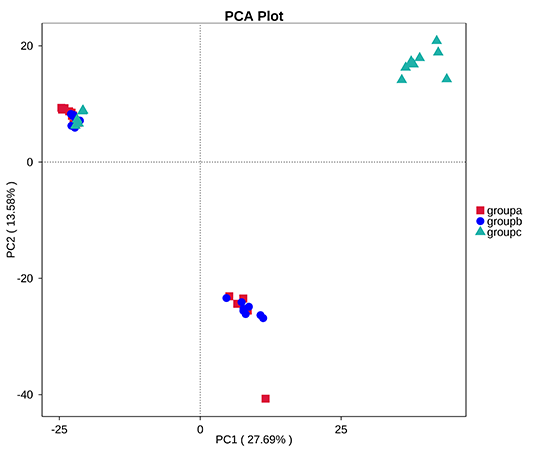
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) based in OTUs
UPGMA Cluster Tree based on Weighted Unifrac Distance

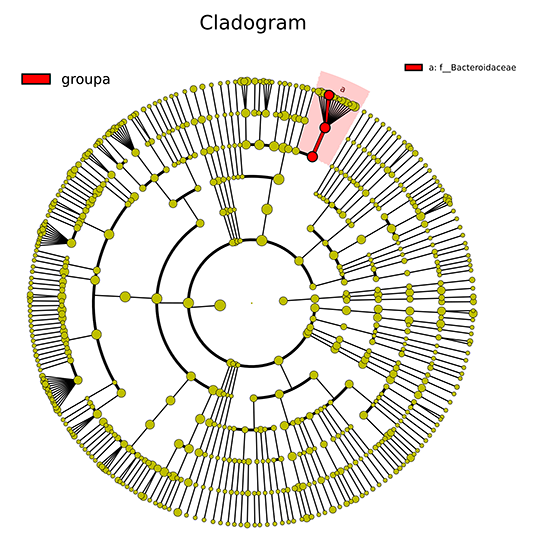
Cladogram of LEfSe Analysis
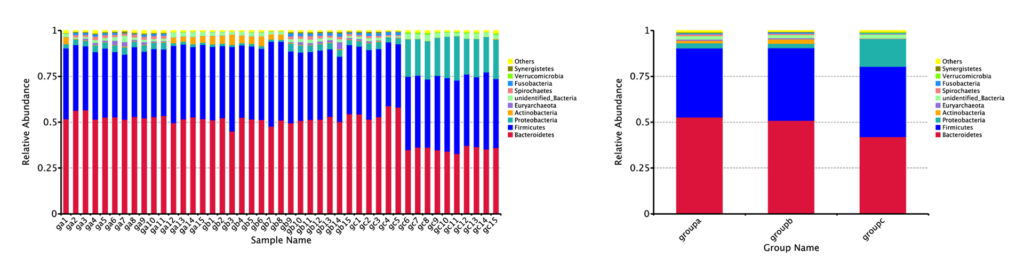
Relative Abundance on Phylum
More Research Services