Kickstart Your Whole Exome Sequencing Project with Novogene
Whole exome sequencing which targets the protein-coding regions of approximately 20,000 genes, is particularly beneficial for high-throughput genetic analysis of vast mutant groups, and enables to attain more in-depth sequencing insights with more effective and fewer data. No matter what field of study you are in, Novogene is a reliable partner to ensure your work meets the highest scientific standards with our rigorous bioinformatics analysis.

The following workflow contains these steps: sample preparation and quality control (QC), library construction and QC, sequencing, data QC and bioinformatics analysis, facilitating detailed dissection of genetic variations, and unraveling the intricate biological tapestry of human genome. Beyond our research-focused WES service, Novogene also qualified with CLIA/CAP/ISO17025 certifications, ensuring clinical diagnostics with unmatched accuracy and precision.
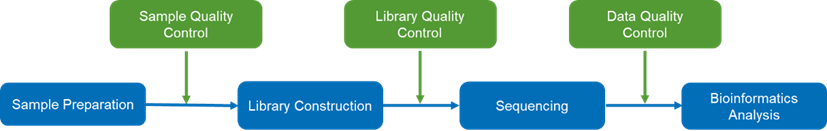
The workflow of whole exome sequencing
- Sample Preparation
Our Whole Exome Sequencing service welcomes human and mouse samples, The format below shows the sample guidelines for research.
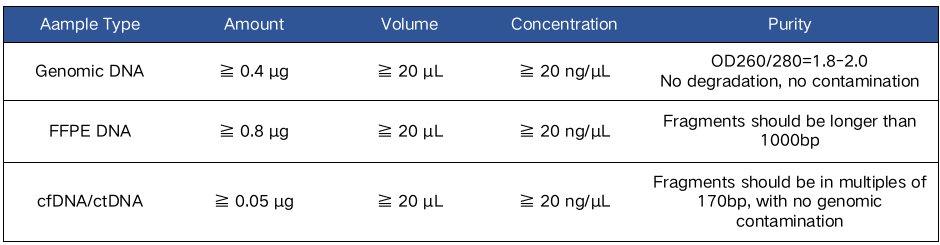
Sample Guidelines for WES
*For clinical WES samples from whole blood, buccal swabs, to saliva, more details can be found in Clinical Whole Exome Sequencing (CLIA/CAP).
- Library Preparation
The genomic DNA was randomly sheared into short fragments with the size of 180-280 bp. For exome capture, we offer multiple hybridization and capture technologies including IDT, Agilent capture kits. - Sequencing
Quantified libraries were pooled and sequenced on Illumina platforms with PE150 strategy. - Bioinformatic Analysis of Standard Package
Raw BCL and FASTQ file output are subjected to data quality control (including QC report outputs) before getting the clean data and further bioinformatic analysis, the bioinformatic analysis pipeline can be showed below.
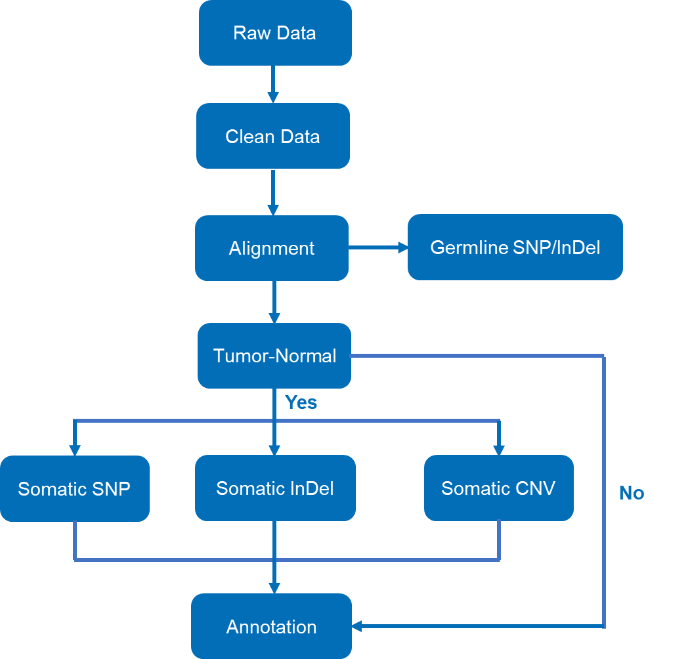
Bioinformatics Analysis Pipeline of Standard Package
- Alignment with reference genome: The process also called mapping, a step that also provides statistics about sequencing depth and coverage. For mendelian disorder or rare disease, the recommended coverage is above 50×, and for tumor sample, the effective coverage should be above 100×.
- Germline mutation detection: This is regularly used to check for inherited predispositions in certain types of cancer or to find the cause of disease in a patient with a genetic disorder, like SNV/SNP and InDel calling.
- Somatic mutation detection: Novogene offers free analysis for somatic variants detection if tumor-normal paired samples are provided. The comparison allows to rule out all the variants that exist in both tumor and control samples, making it easier to detect tumor-specific SNVs or InDels, and also allowing for the detection of copy number variants (CNVs).
- Advanced Analysis for Specific Studies
- For Cancer Research:
- Tumor progression: WES analysis can be used to detect subclones within a tumor tissue, and estimate the proportion of tumor cells (purity), and the absolute copy number of the tumor genome (ploidy). The evolutionary relationship between tumor samples can be analyzed.
- Mutational profiling: Molecular profiling is a standard technique for classifying tumors which may yield clinically relevant diagnostic and prognostic information. Advanced WES analysis can provide information about the key genes and pathways that are critical for tumor initiation and progression, and can also find the relationships among mutated genes.
- Discovery of driver genes: Tumor cells usually contain large numbers of somatic variants, but only few of these mutations drive tumor development. WES can be used to identify driver genes based on mutation clustering bias.
- Xenograft tumor analysis: Patient derived xenograft models (PDX) are often used for developing drugs and precision medicine research. By mapping to the combined murine/human reference genome and further filtering for reads that align to the human genome, all types of tumor information can be obtained, such as SNVs, InDels and much more.
- For Genetic Diseases Research:
- The in-depth analysis of genetic diseases can include candidate variant identification, prioritization of candidate genes or de novo mutation analysis via Trio or Quartet sequencing, in which the patient’s exome is compared to the exomes of their biological parents or other close relatives.
- For Cancer Research:
In summary, the cost-effectiveness makes WES often the preferred method to detect disease-associated variants in prenatal testing and newborn screening, as well as for the identification of rare diseases. And its targeted sequencing approach makes WES a very useful technique to determine hereditary cancer risk or to determine the mutational profile of tumors. Additionally, whole exome sequencing can also be used to explore the distribution and changes of genetic traits within populations to better understand the role of genetics in complex traits, such as susceptibility to certain diseases.
Novogene provides comprehensive whole exome sequencing with a high-quality, affordable and convenient solution with advanced WES analysis, making it possible for WES in a wide variety of applications. So, get ready and push the boundaries of what’s possible with Novogene’s WES services!
Reference:
Pollard KS, Hubisz MJ, Rosenbloom KR, Siepel A. Detection of nonneutral substitution rates on mammalian phylogenies. Genome Res. 2010;20(1):110-121. doi:10.1101/gr.097857.109 (phyloP)
Rentzsch P, Witten D, Cooper GM, Shendure J, Kircher M. CADD: predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D886-D894. doi:10.1093/nar/gky1016 (CADD)
Reva B, Antipin Y, Sander C. Predicting the functional impact of protein mutations: application to cancer genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(17):e118. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr407 (MutationAssessor)