A basic guide to RNA-sequencing
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is the modern, second revolution and the spearhead of an ever-accelerating field. The NGS technology performs innovative research in a variety of different areas, such as: BioPharm, Population genetics/genomics, Agriculture, Forensics, Water testing, Complex and Infectious disease research and etc. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) must be the most mature one of NGS. Here is what you need to know to begin using this tool.
Choosing the right RNA-Seq
Choosing the right RNA-Seq depends on your research question and you first need to understand what type of RNA you are studying. In eukaryotic total RNA, there are various types of RNA molecules, such as:
1. ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – 80-90% of total eukaryotic RNA is in fact rRNA
2. transfer RNA (tRNA)
3. messenger RNA (mRNA) – only 3-7% total eukaryotic RNA represents the protein coding mRNA
4. non-coding RNA (ncRNA), such as for instance:
– long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)
– circulatory RNA (circRNA)
– micro RNA (circRNA)
So how can you know what type of RNA you wish to study? To do that, you need to consider your research objectives: for instance, some projects are interested ‘only’ in comparing transcriptomic profiles across samples in different experimental conditions (e.g Treatment vs. Control), or between different tissue types, to identify tissue-specific gene expression. Other research groups might be more interested in analyzing a shift in cellular transcriptomic footprints across time to determine the time-scale gene expression patterns.
When it comes to transcript profiling, there are three major questions you would wish to answer. One of them is Annotation – a step where you assign function to your RNA molecules. An important aspect to keep in mind is that when analyzing mRNA-Seq data originating from eukaryotic organisms, various isoforms are formed in a process called alternative splicing, and you might want to consider sequencing the different splice variants as well. The second thing you want to do is Quantification of target RNA molecules – crucial for the differential gene expression analysis, where you aim to determine which genes are upregulated/downregulated across your samples. Lastly, one can also perform Target prediction/network study – particularly important when working with non-coding RNA molecules, where you aim to investigate the potential interaction between various RNA molecules, and what are the potential targets of these ncRNAs.
Now that we know all this, you might want to ask yourself what sequencing technologies are available? As a sequence service provider, at Novogene we have the most advanced sequencing platforms to cater to diverse sequencing needs. One of these platforms is the NovaSeq6000 short-read sequencing machine, the most commonly used NGS sequencer which can sequence all types of RNA molecules (up to 500 bp). We also use long-read sequencing Nanopore and PacBio platforms, capable of sequencing up to 10kB in length. However, these platforms can only be used to sequence eukaryotic mRNA molecules containing a polyA tail.
While opting for long-read sequencing approaches may intuitively seem like a better option since full-length transcripts are obtained (meaning that no short-read assembly is required), and PCR bias and input RNA fragmentation are avoided, it is important to note that there are also some disadvantages that need to be considered before deciding to deploy this method. These cons include high error rates, extremely high sample requirements, and the fact that quantification still needs to be done with short-read NGS data.
Service workflow
So how can Novogene help you conduct your research? At Novogene, we have established an end-to-end service workflow and provide our customers with high quality data, publication ready analysis services and offer personalized assistance in collaboration with our highly-skilled team members. All this allows us to assist our customers at any stage of their research project.
As for the RNA-Seq protocol in particular, our services include:
- total RNA extraction
– Sample quality check (QC)
- Library construction
– Library QC
- Sequencing
– Sequence QC
- Bioinformatic analysis
Let’s start from the beginning! How can you prepare your RNA samples? One of the methods we recommend at Novogene to extract total RNA is the TRIzol method which works by maintaining RNA integrity during tissue homogenization, while at the same time disrupting and breaking down cells and cell components. There is also a wide variety of commercially available RNA extraction kits which are often easy to use.
Upon successful RNA extraction, you are ready to send us your samples! We recommend dry ice packaging to do this, and we suggest to consider the amount of dry ice needed for the shipment, as normally 5kg of dry ice is consumed per day. Your samples can be shipped using your preferred courier service, such as for instance through FedEx or DHL, and our Account Managers will be happy to provide you with guidance at any stage of the shipping procedure!
Upon receival of the samples, we will perform the sample quality check (QC) using (1) 1% Agarose gel electrophoresis, (2) Nanodrop reading to check for RNA amount and purity, and (3) Agilent2100 to check for RNA Integrating Number (RIN). At Novogene, we deploy each of these three methods to check the quality of the data you send to us, thereby ensuring you work only with the highest quality data.
Once we confirm the quality of the extracted total RNA is good, we can move on with the protocol and perform the Library Construction step. The polyA enrichment library preparation procedure is most commonly used when working with mRNA-Seq data and results in the construction of 250-300 bp insert cDNA library, which means your samples are now ready to be sequenced!
In case you wish to analyze additional RNA molecules and not just the mRNAs, the whole transcriptome sequencing protocol might be the best option for you. Additional library preparation steps would need to be performed in this instance, such as, (1) rRNA removal & directional RNA library (to retrieve lncRNA, miRNA and circRNA) and (2) small RNA library preparation, crucial to obtain small RNA molecules. Retrieval of all these non-coding RNAs together with mRNAs might be of interest to you if you are interested in analyzing interactions and regulatory networks between RNA molecules, and the consequence of these processes on the establishment of the (molecular) phenotype.
Once the libraries are prepared, you can move forward with the actual sequencing step. There are various sequencing strategies available, such as the (1) single end (SE) sequencing, and (2) paired end (PE) sequencing methods. The choice of an appropriate sequencing strategy again depends on your research question and the type of RNA molecules you work with, and we recommend:
- PE150 bp strategy for
– mRNA, lncRNA & circRNA-Seq datasets
- SE50 bp strategy for
– sRNA-Seq, and
- PE150 & SE50 strategies for
– whole transcriptome sequencing
In addition, we can also offer you the fast mRNA-Seq service entailing (1) RNA QC, (2) Automated library preparation and (3) Sequencing, with a very fast turnaround time which can be as short as only two weeks!
Setting up your analysis & Results overview
Once you receive your RNA-Seq data back from us, you can move forward with the development of a bioinformatics pipeline, or we can analyze the data for you and provide you with publication ready high-resolution visualizations! In case you want us to develop a bioinformatics pipeline for you, you would only need to (1) name samples and groups in your study, (2) choose an appropriate genome as a reference, and (3) design your comparisons using our template document we will provide.
Either option that you choose to go for, here is a general overview of the data analysis protocol utilized to analyze mRNA-Seq data: (1) Data quality check – a step where low confidence nucleotide base-calls can be identified and removed. You can then (2) Map your data to reference genome – a suitable genome can be chosen either from our Novogene database which contains a wide variety of organisms, or from other publicly available genomic repositories, such as the NCBI/UCSC/Ensembl databases. In this step, we will provide (Table 1) tables with read statistics that contain the percentage of reads that mapped against the reference genome, (Figure 1) a piechart – to inform on the percentage of reads that mapped against intron, exon or intergenic regions of the reference genome, and (Figure 2) a graph which shows the distribution of mapped reads across chromosomes. The next step is the (3) Differential gene expression analysis, where we will visualize the distribution of differentially expressed genes across your samples using high-resolution and publication ready volcano plots and heatmaps. To annotate a function to your genes, one can then perform a (4) Functional analysis by mapping the reads against publicly available protein databases, such as the Gene Ontology db (GO enrichment analysis), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes db (KEGG enrichment analysis), or perform a Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and Protein-Protein interaction studies. Lastly, (5) Structure analysis can also be performed to identify Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs), investigate differences in distribution of indels and deletions across samples (InDel analysis), or analyze splice isoforms (Alternative splicing analysis).
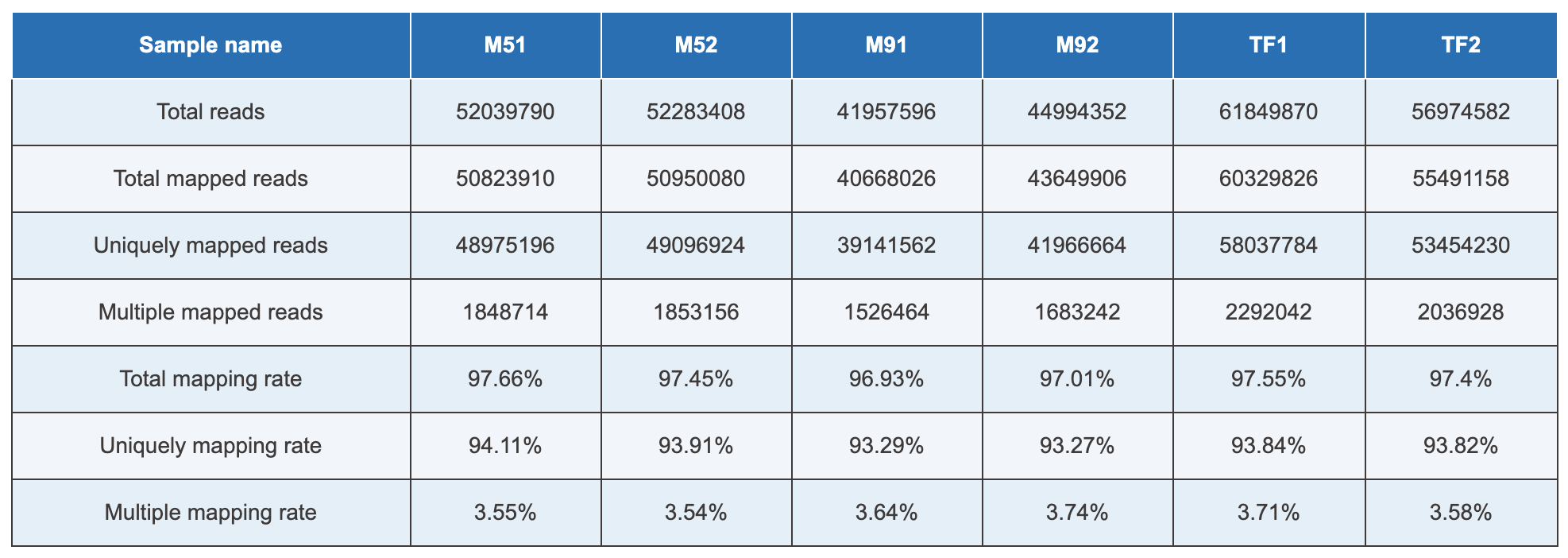
Table 1. Summary of mapping rate
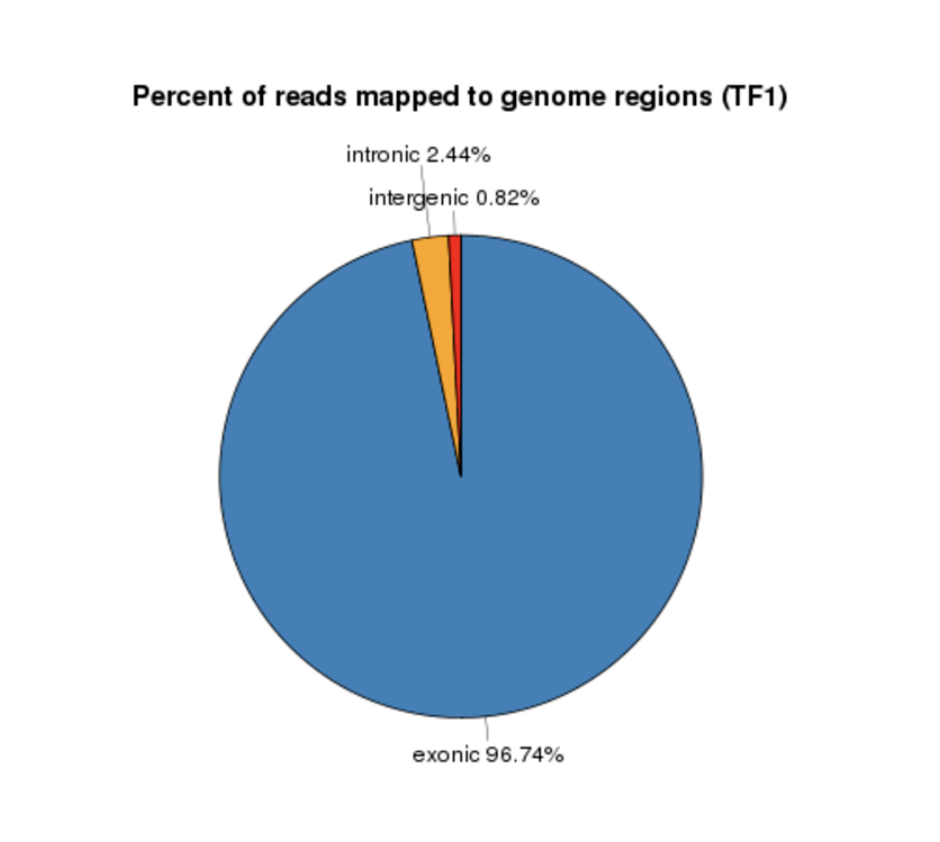
Figure 2. Read distribution on reference genome
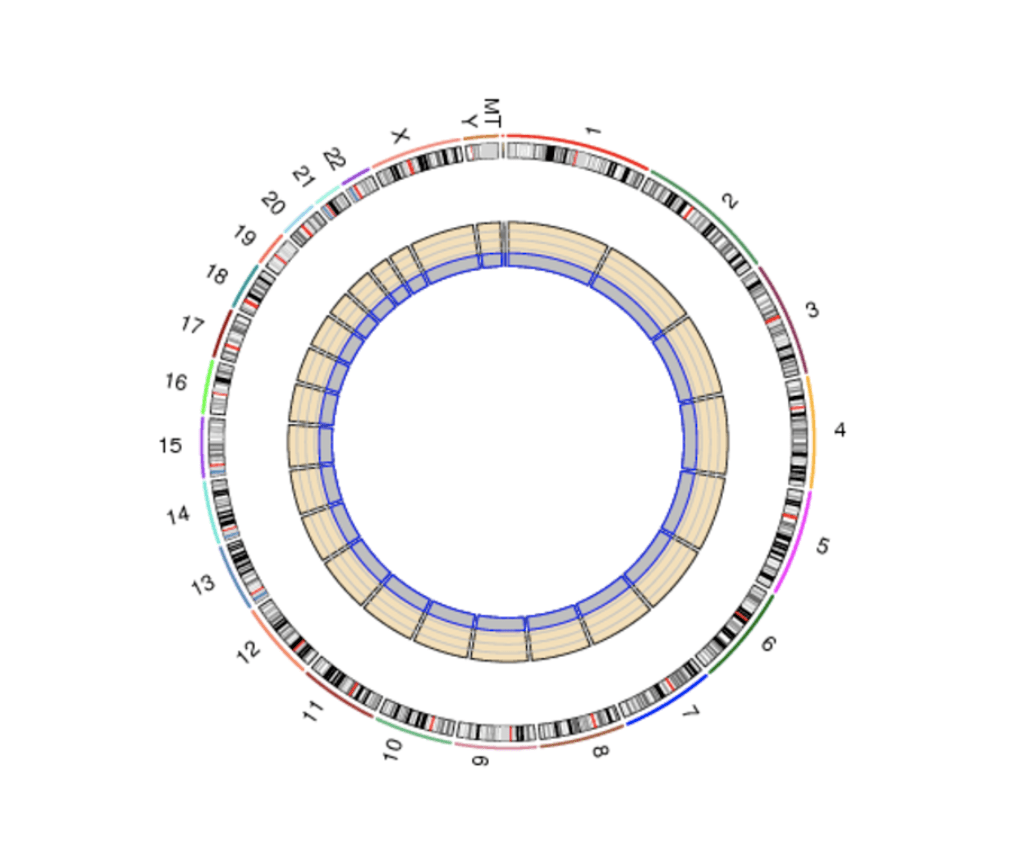
Figure 3. Mapped reads on chromosomes
Novogene RNA-seq
Novogene is a leading provider of genomic services and solutions with cutting edge NGS and bioinformatics expertise, and has the largest sequencing capacity in the world. We pride ourselves in having created 36 NGS related patents and being published in +600 prestigious research papers to date, with a total impact factor of >4270. Additionally, Novogene has a global presence and our facilities are found all across the globe. We provide a variety of services to our clients, such as: (1) DNA services (e.g human genome resequencing / de novo sequencing, microbial community sequencing), (2) Transcriptomic services (messenger RNA (mRNA) sequencing, Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) sequencing, Isoform sequencing, Single-cell RNA sequencing), (3) Epigenetic services (Whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS), ChIP sequencing, RIP sequencing) and (4) Other services (Premade library sequencing, Customized analysis, and etc.).
We hope you enjoyed the blog content, and now feel ready and confident to venture into the world of transcriptomics! Welcome to visit our website novogene.com/us-en to refer more detailed information. Please feel free to contact us in case you are interested to collaborate with Novogene, and hopefully we can be involved in your next publication!