Single-Cell or Single-Nucleus? Nail Your Sample Prep to Win at scRNA-Seq
Pick the wrong suspension and you’ll watch data- and irreplaceable samples-slip away. This is your concise, no-fluff guide to staying on track.
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals biology in breathtaking detail, but every breakthrough starts with one deceptively simple question: Should you prepare single-cell or single-nucleus suspensions? The answer determines whether you hit the jackpot or hit a wall.
I. The Breakdown: Single-Cell vs. Single-Nucleus
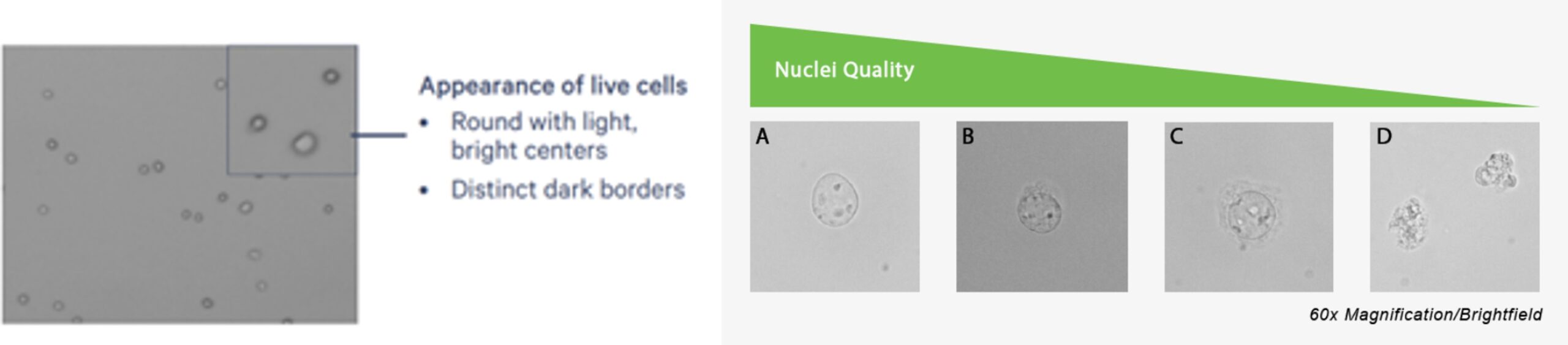
Figure 1. Examples of single-cell suspension (left) and single-nucleus suspension (right)
Single-Cell Suspension (Figure 1, left panel)
- Intact, living cells (membrane + cytoplasm + nucleus)
- Ideal for capturing whole-cell physiology and signaling
Single-Nucleus Suspension (Figure 1, right panel)
- Isolated nuclei released from lysed cells
- Best for focusing on nuclear transcripts, chromatin, and splicing
II. How You Get There
Single-Cell: Start with fresh tissue → enzymatic/mechanical dissociation → cell filtration and wash
Single-Nucleus: Start with fresh, frozen, or FFPE tissue → membrane lysis → nuclear isolation
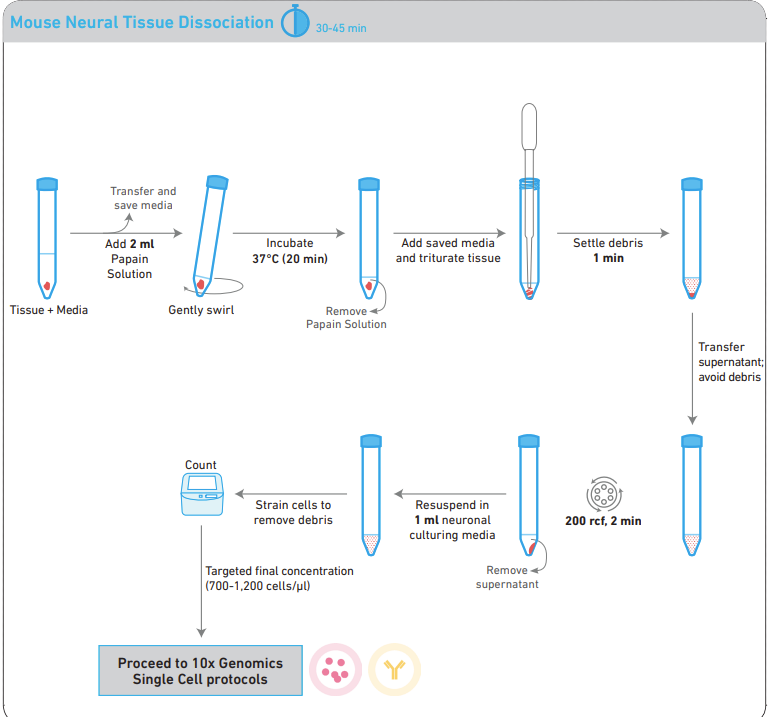
Figure 2. Workflow: Preparing a Cell Suspension from Fresh Tissue
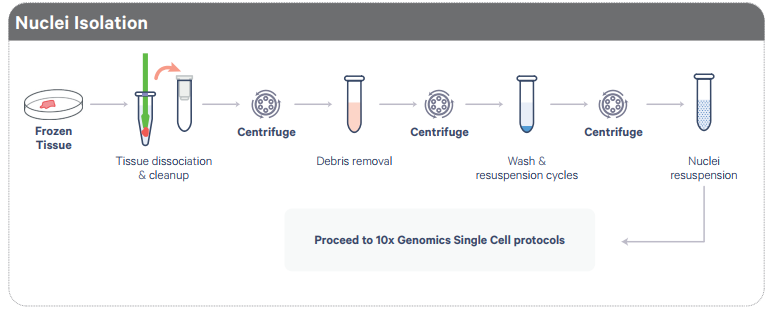
Figure 3. Workflow: Isolating Nuclei from Frozen Tissue
III. When to Use Each—Let the Sample Decide
Choose Single-Cell When
✓ Tissue is fresh and readily dissociated (e.g., blood, marrow, spleen, thymus, many tumors)
✓ Cytoplasmic RNA is required (immune effector molecules, metabolic signatures)
✓ Some cell loss during dissociation is acceptable
Choose Single-Nucleus When
✓ Tissue is frozen, FFPE, or otherwise resistant to dissociation (see Table 1)
✓ You are working with scarce clinical specimens or retrospective samples
✓ The biology of interest centers on nuclear events—transcriptional bursts, splicing, or chromatin regulation
Table 1. Several major tissue and cell types are difficult to dissociate and are therefore unsuitable for preparing single-cell suspensions
| Tissue or Cell Type | Reasons for Unsuitability for Single-Cell Suspension Preparation |
| Brain /Neural | Neurons are highly sensitive, and enzymatic digestion can induce significant expression changes in stress-related genes. Mature neurons are myelinated, and dissociation generates excessive myelin debris, which increases background noise in the suspension. |
| Heart/ Skeletal Muscle/ Adipose Tissue/ Megakaryocytes | Cell diameters are larger than the capture chip channels, preventing successful loading. |
| Liver | Hepatocytes are extremely fragile, and most rupture during processing, resulting in a suspension where they are severely under-represented and do not reflect their true proportion in the tissue. |
| Kidney/ Thyroid/ Pancreas | Structural features, such as abundant endogenous enzymes, make it challenging to obtain high-quality single-cell suspensions. |
| Other tissue types | In drug-resistance studies, samples must be held until patient resistance is assessed, preventing immediate assignment to a study arm. |
| Non-mammalian tissues | Non-mammalian cells have unknown osmolality requirements; standard buffers may cause swelling, lysis, or shrinkage (e.g., marine organisms need high-salt conditions) |
IV. Workflow & Quality Control: Refined Live vs. Standard Live Cells (Table 2)
Table 2. Key Differences in Workflow and QC
| Suspension | Single-Cell | Single-Nucleus |
| Ease of use | Low (tissue-specific optimization) | High (universal protocol) |
| QC Focus | Viability, size, clumps, etc | Nuclear integrity, debris, etc |
V. Data Landscape (Table 3)
Table 3. Key Differences in Bioinformatic Data Characteristics
| Suspension | Single-Cell | Single-Nucleus |
| RNA Source | Cytoplasm + nucleus | Nucleus only |
| Gene Count | Higher | Lower compared to whole-cell suspensions (lacking a large portion of cytoplasmic mRNA) |
| Data Quality Control Metrics | % mitochondrial RNA | % ribosomal RNA |
| Cell Definition | Rely on cytoplasmic markers (e.g., immune cell subtyping) | Depends on nuclear markers (e.g., neuronal subtypes) |
Critical Notice: scRNA-seq and snRNA-seq data are inherently different—do not merge them without specialized bioinformatic methods.
VI. Conclusion: Make the Right Choice from the Start
Single-cell and single-nucleus suspensions are two parallel highways into the single-cell universe, each protecting its own irreplaceable territory. For fresh, easily dissociable tissues, single-cell suspensions let you capture the full dynamic activity of every cell. For frozen or tough-to-dissociate samples, single-nucleus suspensions serve as the master key—sometimes the only key—to unlock the data within.
Keep These Three Golden Rules at the Forefront:
✓ Sample properties—the type and condition of your tissue—drive your decision.
✓ Scientific goals—cytoplasmic function or nuclear regulation—serve as your guiding star.
✓ There’s no “best” approach, only the best fit.
Pick the right prep, and launch your scRNA-seq journey at full throttle!
Appendix:
Table 4. Recommended Dissociation Methods for Common Tissue Types
| Suspension | Single-Nucleus | Single-Cell |
| liver | √(focus on liver parenchyma) | √(focus on immune cells and VDJ) |
| Kidney | √(focus on renal tubules and glomerular podocytes) | √(focus on immune cells) |
| Brain | √(focus on neurons) | √ |
| Adipose tissue / Fat | √(mature adipocyte suspensions are unavailable) | |
| Retina | √ | |
| Heart | √(the diameter of myocardial cells is relatively large) | |
| Spleen | √ | |
| Lung | √ | √ |
| Muscle | √ | |
| Intestine | √ | |
| Blood vessel | √ | |
| Skin | √ | |
| Testis | √ | |
| Uterus | √ | |
| Embryo | √ | |
| Tumor tissue | √ | |
| Esophagus | √ | |
| Bone | √ | |
| Blood | √ |
Why Choose Novogene for Single-cell RNA Sequencing (single-cell RNA-Seq or scRNA-Seq)?
- Proven Expertise: With over 200,000 successfully sequenced samples, Novogene delivers great project results at industry-leading turnaround times. We excel at handling challenging sample types, including nerve and adipose cells.
- Enhanced Sample Processing: We offer a diverse range of sample processing capabilities, including nuclei extraction and specialized pipelines for frozen tissues. This ensures high-quality gene expression data in Single-cell RNA Sequencing (single-cell RNA-Seq or scRNA-Seq) projects.
- Certified Excellence: As a 10x Genomics Certified Service Provider, we leverage the advanced Chromium X platform combined with GEM-X technology for superior reproducibility and efficiency.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: We have state-of-the-art high-throughput sequencing platforms, coupled with expert support, which ensure exceptional data quality and provide cost-effective solutions for single-cell projects.